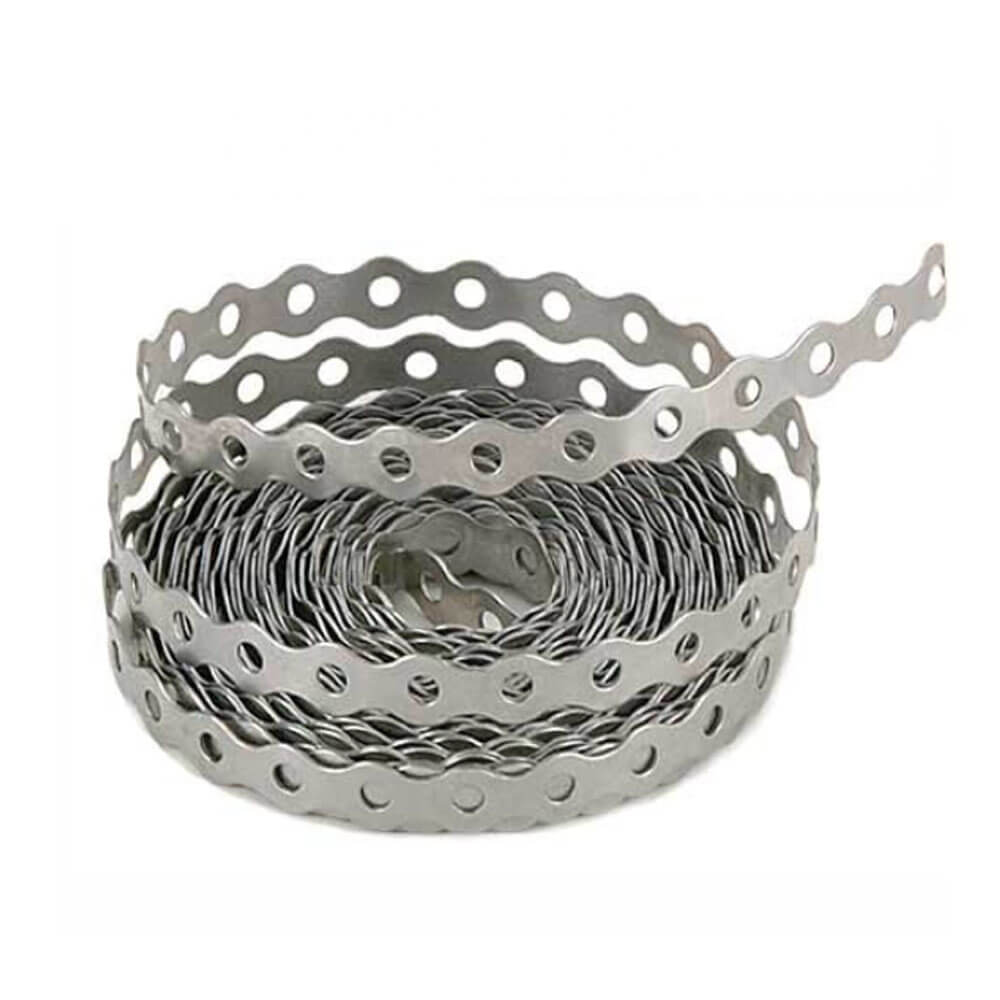
Hanger straps, also known as perforated pipe strapping or perforated hanger straps, are metal strips used to hang pipes, tubes, conduits, ducts, and cables. They provide an inexpensive, lightweight, and adjustable means of support. Hanger straps are available in various materials like steel, stainless steel, galvanized steel, and copper. They come in different shapes, sizes, gauges, and perforation patterns to accommodate different piping systems.

Types of Hanger Straps
There are several types of hanger straps suitable for different applications:
Galvanized Steel Hanger Straps
Galvanized steel is carbon steel coated with a protective zinc layer to prevent rusting and corrosion. Galvanized steel hanger straps are the most common and cost-effective choice. They have good tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Galvanized straps work for indoor applications as well as outdoors when properly sealed and maintained. They come in various perforation designs and thicknesses.
Stainless Steel Hanger Straps
Stainless steel hanger straps contain alloys like chromium and nickel for strength and corrosion resistance. They are suitable for highly corrosive environments like chemical plants, pulp and paper mills, and wastewater treatment facilities. Though costlier than galvanized steel, stainless steel straps have excellent durability and low maintenance requirements. They are also easier to clean and sterilize.
Copper Hanger Straps
Copper hanger strapping provides good corrosion resistance coupled with malleability to bend around pipes easily. Copper naturally inhibits bacterial growth. Hence copper straps are ideal for hospitals, commercial kitchens, breweries, and other hygienic spaces. They are also used in specialized chemical applications. Copper is more expensive but lasts longer than steel.
Plastic Hanger Straps
Plastic pipe straps are made from nylon, polypropylene or other engineered resins. They are lightweight and corrosion proof. Plastic hanger straps suit dry, non-corrosive indoor environments. They can withstand moisture and chemicals better than metal straps. Plastic strapping comes in a range of designs and load capacities.
Perforated Strapping vs Solid Strapping
Perforated strapping has holes punched in the material allowing hanging rods or fasteners to be attached anywhere along the length. This makes perforated straps highly adjustable for different pipe sizes and configurations. It also reduces material usage. Solid strapping has no perforations so hanging clips must be crimped or spot welded in fixed positions. Solid straps provide a smoother surface with no holes for dirt accumulation. Both perforated and solid straps are available for light, medium and heavy load capacities.
Benefits of Using Hanger Straps
There are many good reasons to use hanger straps for your piping supports:
- Cost-Effective: Hanger straps are an economical choice compared to fabricated or welded hangers. Standard straps can be bought off-the-shelf and quickly installed to save time and labor.
- Lightweight: Straps weigh less than rods or angle iron supports. This reduces load on the building structure.
- Adjustable: Multiple hanging points along the strap length allow adjustment to any pipe size. This flexibility facilitates maintenance and future modifications.
- Resists Vibration: Perforated strapping hangs piping loosely to dampen vibrations from equipment or flowing liquids. This prevents noise and pipe fatigue.
- Corrosion Resistant: Galvanized, stainless and copper strapping is highly corrosion resistant for longevity and reliability.
- Easy Installation: Straps can be installed with simple hand tools. They attach using all-thread rods, clips, clamps or fastening strips. No welding or fabricating required.
- Good Looking: Straps have a neat professional appearance compared to improvised wire or chain supports.
- Fire Protection: Galvanized and stainless steel straps withstand fire better than plastic hangers which can melt. This is vital for fire sprinkler systems. Copper and steel also conduct heat away from pipes.
Applications of Hanger Straps
Perforated hanger straps have numerous applications in industrial, commercial and residential settings:
Industrial Facilities
- Process piping in refineries, chemical plants, and mills
- HVAC ducting and air handling systems
- Electrical conduit runs above drop ceilings
- Plumbing pipes -Compressed air lines in factories
Commercial Buildings
- Electrical conduit, cable trays and bus ducts -HVAC ductwork and chilled water lines
- Plumbing pipes in malls, hospitals, schools
- Fire protection sprinkler mains and branch lines
- Network and communication cabling
- Natural gas pipes
Residential Uses
- Electrical wiring in attics and basements
- Home plumbing supply and drainage pipes
- Radiant hot water heating pipes
- Bathroom ventilation ducts
- Clothes dryer vents
- Gas supply lines
Specifying Hanger Straps
Properly specifying and selecting hanger straps ensures correct strength, spacing, and longevity. Consider these factors:
Type of Strap Material
Choose galvanized steel for outdoor use. Select stainless steel or copper for highly corrosive environments. Use plastic strapping for dry indoor applications only.
Pipe Material and Contents
Match strap material compatibility with piping. Some plastics and acids require stainless or plastic strapping. Copper tubes need copper straps.
Pipe Size and Spacing
Size straps to suit pipe diameters. Allow for insulation thickness. Space straps close enough to properly support piping per codes.
System Pressure and Temperature
Higher pressures and temperatures require thicker, stronger straps. Ensure temperature compatibility between fluids and strapping.
Environmental Conditions
If exposed to moisture, sunlight, chemicals, or vibration, select appropriately coated or resistant straps.
Load Capacity
Choose light, medium or heavy duty straps based on piping weight, contents, span lengths, and code requirements.
Perforation Dimensions
Select perforation size, shape and spacing that best facilitates adjustable hanging points. Oval holes allow more adjustment.
Compliance Standards
Specify strapping materials and designs that meet ASTM, ASME, ANSI, MSS, and other applicable standards.
Working with reputable suppliers familiar with hanger strap specifications and building codes ensures correct selection and application.
Installation of Hanger Straps
Perforated hanger iron systems properly installed provide secure, long lasting pipe supports:
Mounting Hardware
Use all-thread rods, U-bolts, wall brackets, or ceiling flanges. Size hardware to handle strap load capacity. Use collar nuts and washers to prevent spinning.
Hanging Methods
Attach straps using friction clips, clamps, riveted brackets, or hook strips. Allow slack for expansion and contraction.
Pipe Attachment
Use plastic pipe saddles, felt padding, or wood blocking to prevent abrasion at hang points. Do not over tighten.
at Hanger Locations
Place hangers at code required intervals based on pipe size and contents. Install additional hangers at valves and equipment.
Pipe Alignment
Maintain pitch for drainage. Use multiple rods for large pipes to prevent straps from twisting or sagging.
Multi-layer Piping
When supporting multiple pipes, place larger pipes below smaller ones and space hangers vertically.
Seismic Forces
In earthquake zones, use rigid channel cross-bracing between piping and the structure.
Thermal Movement
Allow axial movement and use guides to restrain lateral motion. Set hangers at maximum directional movement.
Vibration Isolation
To prevent vibration transmission, run piping through openings slightly larger than pipe diameter and use vibration isolator pads.
Corrosion Protection
Use plastic tape, sleeves, or epoxy coatings to isolate dissimilar metals. Avoid water collection on straps.
Proper installation reduces leaks, prevents damage, and ensures galvanized iron perforated hanger systems meet operational and safety objectives over their full service life.
Maintenance of Hanger Strap Systems
Routine inspection and maintenance makes galvanized hanger strap systems more reliable. Key maintenance practices include:
Visual Inspection
Periodically check for damage, loose hardware, metal deterioration, and debris accumulation. Replace worn parts.
Fastener Tightness
Using a calibrated torque wrench, check and re-tighten loose bolts and nuts which can cause slipping or metal fatigue.
Lubrication
Keep threaded rods and fastener threads clean and lubricated for easy break-out and re-tightening during maintenance.
Pipe Movement
Ensure piping moves freely on hangers without binding during heating/cooling cycles. Adjust hangers or guides as needed.
Pipe Protectors
Replace worn saddles, padding, and isolation strips to prevent pipe damage from vibrations and contact.
Pipe Alignment
Verify piping remains aligned, supported, and not sagging from added weight like insulation or accumulated process solids.
Corrosion Protection
Touch up scratched or exposed metal with matching paint or coatings to prevent deterioration or oxidation.
Overflow Drains
Clear any clogged water drainage holes or channels on straps to prevent overflow corrosion.
Records
Document equipment repairs, upgrades, and replacement parts for future reference.
Proper maintenance safeguards reliability and maximizes the service lifetime of perforated pipe strapping systems. Facilities should develop standard inspection and recordkeeping procedures.
Conclusion
Hanger straps provide an indispensable means to securely hang pipes, tubes, ducts, conduits, and cables in countless industrial and commercial applications. These lightweight, economical perforated hanger straps are available in various configurations and materials to suit diverse strength, corrosion resistance and adjustability needs. Perforated galvanized steel straps meet general needs for low cost and durability. Stainless steel straps withstand highly corrosive conditions. Copper straps add malleability and hygienic properties. Proper specification, installation and maintenance ensures hanger straps safely support piping over its full service life. Hanger straps bring simplicity, flexibility and reliability to pipe hanging tasks.
FAQ
What are the different types of hanger straps?
The main types of hanger straps are galvanized steel, stainless steel, copper, and plastic. Galvanized steel straps are the most common and economical choice. Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance. Copper provides excellent antimicrobial properties. Plastic strapping is lightweight but for dry indoor use only.
How are hanger straps installed?
Hanger straps are installed using threaded rods, U-bolts and ceiling brackets for overhead mounting. They attach to pipes using friction clips, clamps or riveted brackets. Proper hardware sizing, hang spacing, and allowing thermal movement are key installation factors.
What pipe materials work with hanger straps?
Most any pipe material can be hung with straps including steel, copper, plastic, cast iron, fiberglass and more. Straps are commonly used on plumbing, compressed air, HVAC, fire sprinkler, electrical conduit and process piping systems.
How often should hanger straps be inspected?
A visual inspection at least once a year is recommended. Critical systems like steam or hazardous materials piping should be inspected more frequently for any signs of wear, damage, loose hardware, or corrosion.
Why choose hanger straps over other types of pipe hangers?
Advantages of hanger straps include lower cost, light weight, adjustability, vibration dampening, quick installation, neat appearance, and corrosion resistance. They provide a fast, reliable means of suspension.
Perforated Metal Hanger Straps: Installation, Benefits, and Maintenance
Are you tired of dealing with sagging ductwork or unsupported pipes in your home or commercial building? Proper support is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of your HVAC and plumbing systems. That's where perforated metal hanger straps come into...
Galvanized Steel Strapping vs Stainless Steel Strapping: A Comprehensive Comparison
Introduction When it comes to securing and bundling materials, steel strapping is a popular choice due to its strength, durability, and versatility. However, not all steel strapping is created equal. Two of the most widely used options are galvanized steel strapping...
How To Install All Round Steel Strapping?
If you're in the construction or plumbing industry, you know that hanging pipes securely is crucial for a successful installation. One of the most reliable methods for supporting pipes is using all round steel strapping, also known as banding. This versatile material...

Justin Wong
Hi, I’m Justin, the technical engineer of Jiangmen Masters. We’ve been running a factory in China that makes metal hanger strap for 16 years now, and the purpose of this article is to share the knowledge related to metal hanger strap from a Chinese supplier’s perspective.