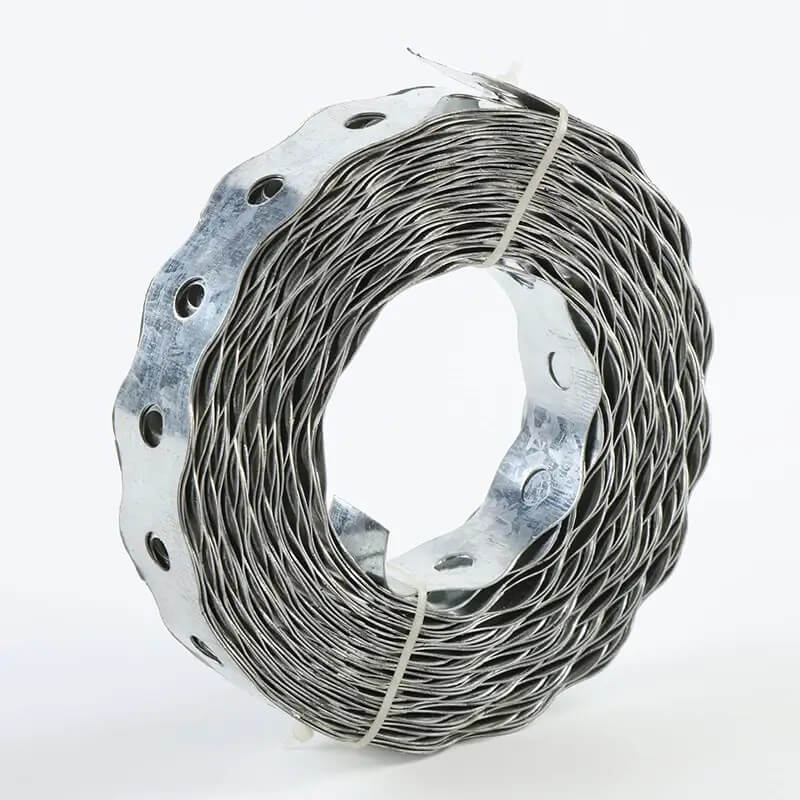
Metal strapping with holes provides an adaptable and heavy-duty fastening solution for a variety of industrial and commercial applications. This guide will explore everything you need to know about metal strapping, from types and applications to proper installation and maintenance best practices. We’ll also compare top brands and summarize key takeaways to ensure you select and use the right metal strapping for your specific needs.

Introduction to Metal Strapping with Holes
Metal strapping, also called metal banding or metal bands, refers to thin strips of metal that can be fastened together to secure items. The addition of holes allows the strapping to be easily bolted, screwed or riveted for extra strength and customization.
Metal strapping with holes is valued for its adjustability, sheer strength, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used for attaching and bracing large, heavy components where vibration, weather, and extreme forces are factors.
Types of Metal Strapping
There are two main categories of metal strapping to consider:
Stainless Steel Strapping
Stainless steel strapping provides unmatched corrosion resistance and durability, even in outdoor and marine environments. Most common grades used are 304 and 316 stainless steel. It has high strength and moderate cost.
Carbon Steel Strapping
Carbon steel strapping is widely used for its strength and lower cost compared to stainless. It is often coated with zinc, paint or vinyl for added corrosion protection. Common grades are hot-dipped galvanized, cold rolled, and painted/PVC-coated.
In terms of width, thicknesses from 1/2” to 2” are typical for strapping with holes. Wider straps may have multiple hole patterns. Thicknesses generally range from 0.015” up to 0.075”.
Applications of Metal Strapping
Thanks to its versatility, adjustable fastening, and weather-resistance, metal strapping has numerous applications:
- Bracing HVAC, plumbing, and electrical systems
- Securing ductwork, conduit, and piping
- Anchoring industrial equipment like compressors
- Attaching signs, frames, and accessories to buildings
- Bundling multiple items like rods or tubes together
- Creating safety rails and barricades
- Building heavy crating or shipping frames
- Temporary bracing during construction and assembly
- Strengthening cargo loads on trucks and shipping containers
Metal strapping with holes is the ideal choice when adjustable, high-strength fastening is needed.
Installation Tips and Best Practices
Properly installing metal strapping ensures safe and secure application:
- Clean surfaces thoroughly before attaching straps
- Use manufacturer hole spacing for uniform look and strength
- Customize strap lengths based on circumference plus overlap
- Allow for thermal expansion/contraction in outdoor uses
- Use washers under bolt heads to prevent pull-through
- Tighten bolts gradually in a crisscross pattern
- Trim excess length but avoid sharp protruding edges
- Consider sealants/protectants for longevity in wet environments
- Inspect initially for secure fit then recheck periodically
Following proper techniques maximizes strength while allowing accessibility for maintenance. Always refer to installation manuals for specific strapping products as well.
Maintenance of Metal Strapping
Like with most industrial components, routine maintenance preserves the longevity and safety of metal strapping:
- Periodically check for loose, damaged or corroded strapping
- Re-tighten or replace compromised strapping immediately
- Clean metal with compatible cleaners to prevent buildup
- Spot repair any scratches/chips with touch-up paint
- Lubricate threads of bolts/screws to prevent seizing
- Verify compatibility with any sealants, paints or chemicals before use
- Remove corrosion, treat underlying cause (i.e. water intrusion)
- Monitor painted/coated straps for finish wear
Proper maintenance lets you identify potential issues early and prevent catastrophic failures down the road.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Should problems arise with your metal strapping, here are some typical issues and solutions:
Corrosion – For light corrosion, clean and apply protective sealant. Replace severely corroded straps. Improve water drainage if outdoors.
Loose Straps – Re-tighten straps to proper torque. Replace damaged fasteners. Verify load weights haven’t exceeded capacity.
Damaged/Bent Strapping – Repair or replace straps that are cracked, warped or punctured. Check attached components for damage.
Compromised Finish – Spot repair paint/coatings chips. Fully repaint areas with excessive coating wear.
Excess Vibration – Ensure tight, uniform installation. Add vibration dampening accessories if needed. Check load balances.
Loads Shifting – Increase strap overlaps, add more attachment points, and reduce spacing between fasteners.
Metal Fatigue – Gradually replace fatigued straps showing signs of work hardening or microcracking.
Diagnosing and addressing issues quickly maintains safety and security. Enlist metal fabrication experts as needed.
Key Considerations When Selecting Metal Strapping
To select the ideal strapping, keep in mind:
- Application and expected loads
- Environmental factors like weather, saltwater, chemicals
- Size of components being fastened
- Total lengths needed and desired hole spacing
- Aesthetic preferences for coated/plated/etched finishes
- Code compliance and regulatory requirements
- Budget
Careful thought must be given to these factors to match the optimal strapping configuration to the intended service conditions and installation.
Conclusion
With its versatility and strength, metal strapping with holes provides an adaptable fastening solution for industrial and commercial uses where vibration, humidity and heavy loads demand reliable fastening. Following the tips in this guide allows you to properly select, install and care for metal strapping to leverage its full potential while minimizing maintenance costs. Connect with fabrication specialists for added insight on choosing strapping that fully suits your unique application requirements. Properly implemented metal strapping delivers adjustable and long-lasting performance.
FAQ
Q: Is metal strapping rustproof?
A: Carbon steel strapping can rust if uncoated. Stainless steel and coated carbon steel offer corrosion resistance. Proper maintenance is still required.
Q: What tools are needed to install metal strapping?
A: Hand tools like pry bars, wrenches, snips, and drills, plus power tools like impact drivers and hole punch tools. Strapping tensioners for non-punched straps.
Q: Can I reuse metal strapping when removing equipment?
A: It’s not advisable to reuse strapping as tightening and vibration can compromise integrity. New strapping ensures proper fastening.
Q: What are common metal strapping sizes?
A: Widths range from 1/2″ to 2″. Thicknesses span 0.015” to 0.075” typically. Hole spacing varies by application. Overall length depends on use.
Q: Is galvanized or stainless steel better for outdoor use?
A: Galvanized offers the most corrosion resistance for continually wet, salty or corrosive outdoor environments.
Secure Your Pipes with Galvanized Metal Straps: A Comprehensive Guide
Ensuring Pipe Stability and Longevity In the world of construction and plumbing, maintaining the structural integrity of piping systems is paramount. Galvanized metal pipe straps emerge as the unsung heroes, providing unwavering support and security to these vital...
Mastering 24 Gauge Galvanized Pipe Hanger Straps: A Useful Guide
In the realm of plumbing and construction, where every detail matters, securing pipes effectively is paramount. Enter the 24 gauge galvanized pipe hanger strap – a reliable and versatile solution trusted by both professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. Understanding...
Perforated Metal Hanger Straps: Installation, Benefits, and Maintenance
Are you tired of dealing with sagging ductwork or unsupported pipes in your home or commercial building? Proper support is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of your HVAC and plumbing systems. That's where perforated metal hanger straps come into...

Justin Wong
Hi, I’m Justin, the technical engineer of Jiangmen Masters. We’ve been running a factory in China that makes metal hanger strap for 16 years now, and the purpose of this article is to share the knowledge related to metal hanger strap from a Chinese supplier’s perspective.